The combination of technology and fitness has been one of the most transformative developments in personal health management in recent years, with wearable technology leading the charge towards a more personalized and data-driven approach to fitness. As devices become increasingly sophisticated, they offer users a deeper understanding of their bodies and activities, enabling tailored fitness programs that were once the realm of professional athletes and specialized medical practitioners. The evolution from basic step counters to advanced biometric monitoring devices signifies not just a technological advancement but a paradigm shift in how individuals engage with their health and wellness routines.
The origins of wearable fitness technology can be traced back to simple pedometers, devices that primarily counted steps and estimated distance traveled. These early tools provided users with a rudimentary measure of their daily activity levels, serving as a catalyst for increased movement and awareness of sedentary habits. While beneficial, these devices offered limited insights, lacking the capability to capture the complexities of human physiology and the myriad factors influencing health and performance. Recognizing the potential for deeper engagement, innovators began integrating more advanced sensors and computational power into wearables, paving the way for a new generation of devices capable of comprehensive health monitoring.
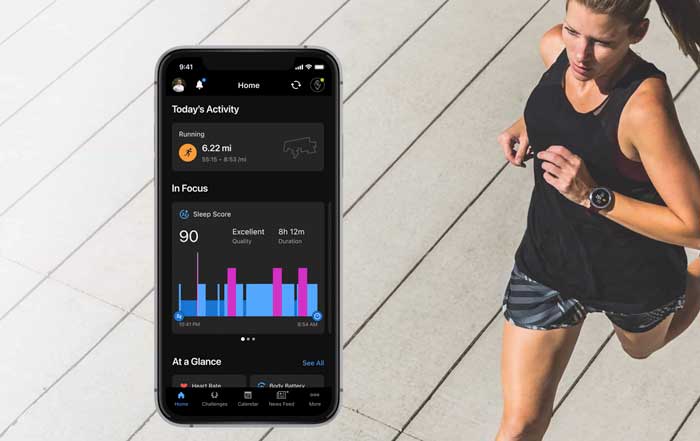
Modern wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are equipped with an array of sensors that collect data on various physiological parameters, including heart rate, blood oxygen levels, sleep patterns, and even stress indicators. These devices utilize photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors to measure heart rate by detecting blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, providing continuous heart rate monitoring throughout the day. Accelerometers and gyroscopes track movement and orientation, enabling the accurate capture of steps taken, distance traveled, and even specific types of physical activity, such as cycling or swimming.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into wearable technology has significantly enhanced the personalization of fitness experiences. By analyzing the vast amounts of data collected, AI can identify patterns and trends unique to each user, offering personalized recommendations and insights. For example, if the data indicates that a user consistently performs better in the mornings, the wearable device might suggest scheduling workouts during that time to maximize performance. Similarly, machine learning can predict potential overtraining by recognizing deviations in resting heart rate or sleep quality, prompting users to incorporate rest days into their routines.
One of the critical benefits of wearable technology in personalized fitness is the real-time feedback it provides. Users receive instantaneous data on their performance metrics, allowing for immediate adjustments to their activities. During a workout, a runner can monitor their pace, heart rate, and stride length, making on-the-fly adjustments to optimize performance. This immediacy enhances the effectiveness of training sessions, as users are not reliant on post-activity analysis to make improvements. Moreover, the ability to monitor physiological responses during exercise can prevent injuries by alerting users when they are pushing beyond safe limits.
Sleep tracking is another area where wearable technology has made significant strides, recognizing the vital role that rest and recovery play in overall health and fitness. Advanced wearables can track sleep stages, including light, deep, and REM sleep, providing insights into sleep quality and duration. Poor sleep can negatively impact performance, recovery, and general well-being. By understanding their sleep patterns, users can make lifestyle adjustments to improve sleep hygiene, such as establishing consistent bedtime routines or reducing screen time before bed.
Stress monitoring features in wearable devices leverage heart rate variability (HRV) measurements to assess the body's stress levels. HRV is the variation in time between consecutive heartbeats, and it is a sensitive marker of autonomic nervous system activity. A lower HRV indicates higher stress levels, while a higher HRV suggests a more relaxed state. By monitoring stress levels throughout the day, users can identify stress triggers and implement coping strategies, such as mindfulness exercises or deep-breathing techniques, to manage stress effectively.
The social aspect of wearable technology also contributes to personalized fitness by fostering a sense of community and accountability. Many devices and associated apps allow users to connect with friends, join challenges, and share achievements. This social connectivity can motivate individuals to stay committed to their fitness goals, as they receive encouragement and recognition from their peers. Additionally, the competitive element introduced through leaderboards and challenges can inspire users to push themselves further than they might on their own.
The integration of wearable tech with nutrition and diet tracking apps further enhances the personalization of fitness programs. By logging food intake and comparing it with activity levels, users can achieve a more holistic understanding of their energy balance and nutritional needs. Some wearables can estimate calorie expenditure based on activity data, helping users make informed decisions about their diet to support their fitness goals, whether that is weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance.
Advancements in sensor technology have led to the development of wearables capable of measuring more complex health indicators. Devices that monitor blood glucose levels non-invasively are particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes, allowing for continuous glucose monitoring without the need for frequent finger-prick tests. Similarly, wearables that can detect blood pressure fluctuations provide users with critical information about their cardiovascular health, enabling early detection of potential issues.
The potential of wearable technology in fitness extends into the realm of personalized coaching and virtual training. AI-powered virtual coaches can provide tailored workout plans based on the user's data, adjusting routines in response to progress and feedback. These virtual coaches can offer exercise demonstrations, technique corrections, and motivational support, replicating many aspects of a personal trainer at a fraction of the cost. The convenience of having access to expert guidance anytime and anywhere makes fitness more accessible and adaptable to individual schedules.
As wearable technology continues to evolve, the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a significant role in creating interconnected ecosystems of devices. Wearables can communicate with other smart devices, such as home gym equipment, smart scales, and even kitchen appliances. This interconnectedness allows for seamless integration of various aspects of health and fitness, providing a comprehensive picture of an individual's lifestyle. For instance, a smart refrigerator could suggest meal options based on the user's nutritional needs and activity levels, while a smart treadmill could adjust workout intensity based on recovery status indicated by the wearable device.
Data analytics and cloud computing are essential components supporting the functionality of wearable technology. The vast amounts of data generated by wearables require robust storage and processing capabilities to extract meaningful insights. Cloud-based platforms enable the aggregation and analysis of data from multiple sources, facilitating advanced analytics and machine learning applications. This infrastructure not only supports individual users but also contributes to broader health research by providing anonymized data sets that can inform public health initiatives and medical studies.
The role of wearable technology in preventive health care is another area of significant impact. By monitoring key health indicators, wearables can detect anomalies that may indicate the early stages of medical conditions. For example, irregular heart rhythms detected by ECG-capable wearables can prompt users to seek medical attention before more severe symptoms develop. This proactive approach to health care can lead to earlier diagnoses, more effective treatments, and better health outcomes.
Despite the numerous benefits, wearable technology in fitness also presents challenges and considerations that need to be addressed. Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, given the sensitive nature of health information collected by these devices. Manufacturers and service providers must implement robust security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access and breaches. Transparency in data handling practices and compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are essential to build and maintain user trust.
Another challenge is the potential for data overload and analysis paralysis among users. The sheer volume of data generated can be overwhelming, and without proper context or understanding, users may struggle to interpret the information effectively. Simplifying data presentation through intuitive interfaces and providing actionable insights rather than raw data can enhance user experience and engagement. Educating users on the significance of various metrics and how they relate to their fitness goals is crucial in maximizing the benefits of wearable technology.
The issue of accuracy in wearable devices remains a topic of discussion. While technology has advanced, discrepancies can still exist between measurements from wearables and clinical-grade equipment. Factors such as device placement, user movement, and sensor limitations can affect data accuracy. Continuous research and development are necessary to improve sensor technology and algorithms, ensuring that users receive reliable information to base their fitness decisions upon.
Evolution of Wearable Fitness Technology
Accessibility and inclusivity are also important considerations in the adoption of wearable technology. High-end devices with advanced features may be cost-prohibitive for some individuals, potentially exacerbating health disparities. Efforts to produce affordable wearables without compromising essential functionalities are necessary to democratize access to personalized fitness tools. Additionally, designing devices that are user-friendly for individuals with disabilities or varying levels of technological proficiency is essential to ensure that the benefits of wearable technology are available to all.
Looking ahead, the future of wearable technology in personalized fitness is poised to be shaped by several emerging trends and innovations. The development of flexible and stretchable electronics opens possibilities for wearables that conform more naturally to the body, such as smart clothing and patches. These form factors can provide more accurate data by maintaining better contact with the skin and can monitor a wider range of physiological signals unobtrusively.
Advancements in battery technology and energy harvesting methods are expected to enhance the usability of wearables by extending battery life or eliminating the need for charging altogether. Technologies such as solar cells integrated into wearables or kinetic energy harvesting from body movement can provide sustainable power solutions, improving convenience and reducing environmental impact.
The integration of wearable technology with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) platforms is anticipated to revolutionize fitness experiences. AR glasses or headsets can overlay digital information onto the real world, providing interactive workout guidance, form corrections, and immersive training environments. VR can transport users to virtual settings for workouts, making exercise more engaging and enjoyable, which can enhance adherence to fitness programs.
Biofeedback and neurofeedback technologies represent another frontier in wearable tech. Devices capable of monitoring brainwave activity can provide insights into mental states, such as focus, relaxation, and stress levels. By understanding and training these mental aspects, users can enhance performance, manage anxiety, and improve overall mental well-being. The incorporation of mindfulness and meditation practices into fitness routines acknowledges the holistic nature of health, encompassing both physical and mental components.
Collaboration between wearable tech companies and healthcare providers is expected to grow, integrating personal fitness data into medical care. Electronic health records (EHRs) that include data from wearables can provide healthcare professionals with a more comprehensive view of a patient's health, enabling personalized treatment plans and proactive interventions. This integration raises important considerations around data privacy, consent, and interoperability standards, necessitating careful navigation to ensure ethical and effective utilization of data.
The use of blockchain technology in wearable tech data management is an emerging solution to enhance security and control over personal data. Blockchain can provide decentralized and immutable records of data transactions, giving users greater transparency and authority over how their information is shared and used. This approach can address some of the privacy concerns associated with centralized data storage and foster greater trust in wearable technology platforms.
In the realm of sports and athletic performance, wearable technology is advancing towards providing real-time biomechanical analysis. Devices equipped with advanced sensors can capture detailed movement patterns, joint angles, and muscle activation levels. This data can inform technique improvements, injury prevention strategies, and performance optimization for athletes at all levels. By bringing such capabilities to consumer wearables, individuals can benefit from professional-level insights in their personal fitness endeavors.
Environmental monitoring is another area where wearable tech is expanding. Devices that can measure air quality, UV exposure, and other environmental factors can help users make informed decisions about outdoor activities. By understanding the environmental conditions that may affect health and performance, individuals can adjust their plans to optimize safety and effectiveness.
The ethical considerations surrounding wearable technology continue to evolve as the capabilities and applications of these devices expand. Issues such as data ownership, informed consent, and the potential for surveillance require ongoing dialogue among stakeholders, including users, manufacturers, policymakers, and ethicists. Establishing clear guidelines and regulations that balance innovation with individual rights is essential to ensure that wearable technology develops in a manner that benefits society as a whole.
In educational settings, wearable technology has the potential to enhance physical education programs by providing students with personalized feedback and promoting engagement. Teachers can utilize data to tailor activities to individual fitness levels and monitor progress over time. Incorporating technology into education can also foster digital literacy and encourage students to take an active interest in their health from a young age.
Corporate wellness programs are increasingly incorporating wearable technology to promote employee health and productivity. By offering wearables as part of wellness initiatives, companies can encourage physical activity, stress management, and healthy habits among their workforce. This approach can lead to reduced healthcare costs, improved employee satisfaction, and enhanced overall organizational performance.
In conclusion, wearable technology represents a transformative force in the realm of personalized fitness, offering unprecedented opportunities for individuals to engage with their health in meaningful and impactful ways. The ability to monitor a wide array of physiological parameters, receive real-time feedback, and access personalized coaching empowers users to take control of their fitness journeys with a level of precision and adaptability previously unattainable. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications and benefits of wearable tech in fitness are vast, promising a future where personalized health and wellness are seamlessly integrated into daily life.
The challenges associated with data privacy, accuracy, accessibility, and ethical considerations are significant but not insurmountable. Through collaborative efforts among industry leaders, regulators, and consumers, solutions can be developed to address these issues, ensuring that the evolution of wearable technology proceeds in a manner that is beneficial, equitable, and respectful of individual rights.
Embracing wearable technology in personalized fitness is more than adopting new gadgets; it signifies a commitment to proactive health management and a recognition of the integral role that technology can play in enhancing quality of life. Whether for the casual fitness enthusiast or the professional athlete, wearable tech offers tools that can inspire, motivate, and guide individuals towards achieving their health and wellness goals. The future of personalized fitness is not just about tracking metrics but about transforming data into actionable insights that foster sustainable, healthy lifestyles.
As society becomes increasingly health-conscious, the demand for personalized fitness solutions will continue to grow. Wearable technology is poised to meet this demand, offering innovative and user-centric approaches that align with the diverse needs of individuals. The convergence of technology, health, and personalization represents a significant stride towards a future where optimal wellness is accessible to all, supported by the seamless integration of wearable tech into the fabric of everyday life.